Breathing apparatus cylinders, commonly used in firefighting, diving, and rescue operations, are essential safety tools designed to provide breathable air in hazardous environments. These cylinders are made from different materials, each chosen for its ability to store air at high pressures while being durable and safe for use. The three primary materials used in manufacturing breathing apparatus cylinders are aluminum, steel, and composite materials, often with a glass or carbon fiber wrap.
This article will explore the different materials used in the construction of breathing apparatus cylinders, focusing particularly on the advantages of carbon fiber composite cylinders, which are becoming increasingly popular due to their lightweight yet robust nature.
Aluminum Cylinders
Aluminum was one of the first materials used in the manufacturing of breathing apparatus cylinders. These cylinders are widely used today due to their relatively lightweight nature compared to steel and their corrosion-resistant properties.
Advantages:
- Lightweight: Aluminum cylinders are lighter than steel, which makes them easier to carry, especially in demanding situations like firefighting or rescue missions.
- Corrosion-Resistant: Aluminum is naturally resistant to corrosion, making it suitable for environments where the cylinder might be exposed to moisture or chemicals.
- Cost-Effective: Aluminum cylinders are generally more affordable than composite options, making them an attractive choice for some users.
However, aluminum cylinders are not the lightest option available, and for applications where weight is a critical factor, such as in SCBA (Self-Contained Breathing Apparatus) systems or for use in extended operations, other materials may be more advantageous.
Steel Cylinders
Steel was traditionally the material of choice for breathing apparatus cylinders due to its durability and strength. Steel cylinders can withstand high pressures and are exceptionally sturdy, making them a reliable option in extreme conditions.
Advantages:
- Durability: Steel cylinders are highly durable and resistant to impacts, which makes them a good choice for harsh environments.
- Pressure Resistance: Steel can handle very high pressures, ensuring that the cylinder remains safe and operational even under the most demanding conditions.
Drawbacks:
- Heavy: Steel cylinders are significantly heavier than aluminum or composite cylinders, which can make them cumbersome to carry, especially for longer periods.
- Prone to Corrosion: Despite its strength, steel is more prone to corrosion than aluminum or composites, so steel cylinders require more maintenance, particularly in humid or corrosive environments.
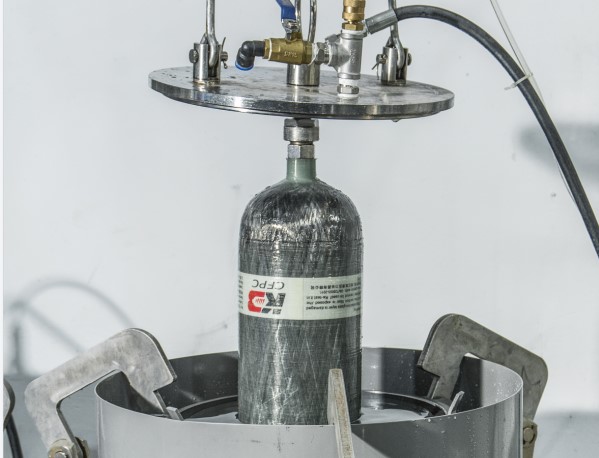
Carbon Fiber Composite Cylinders
In recent years, the use of composite materials, especially carbon fiber, has revolutionized the design of breathing apparatus cylinders. Carbon fiber composite cylinders are made by wrapping an aluminum or plastic liner with layers of carbon fiber, often combined with resin. These cylinders offer the highest strength-to-weight ratio of any cylinder material, making them an excellent choice for applications where both performance and mobility are key.
Advantages:
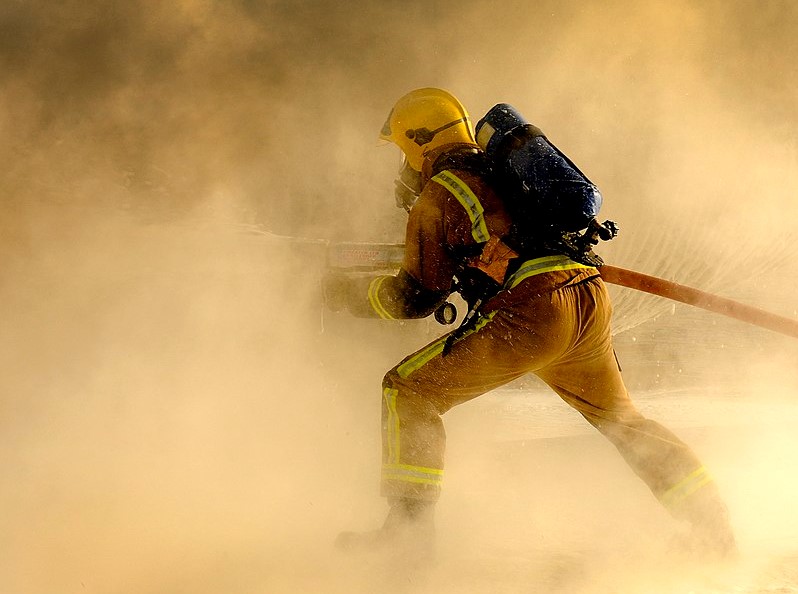
- Extremely Lightweight: Carbon fiber composite cylinders are much lighter than both steel and aluminum cylinders. For users who need to move quickly or carry their equipment for extended periods, such as firefighters or rescue personnel, this reduction in weight can make a significant difference.
- Strength and Durability: Despite their light weight, carbon fiber composite cylinders are incredibly strong and can handle the same, or even higher, pressures as steel or aluminum cylinders. The carbon fiber wrap provides extra reinforcement, allowing the cylinder to withstand impacts and other stresses without compromising its integrity.
- Corrosion Resistance: Like aluminum, carbon fiber composite cylinders are resistant to corrosion, making them suitable for a wide range of environments, including those with high humidity or exposure to chemicals.
Drawbacks:
- Higher Cost: Carbon fiber composite cylinders are more expensive than aluminum or steel options, which can be a limiting factor for some organizations. However, the benefits of reduced weight and increased durability often outweigh the higher initial investment for many users.
- Complex Manufacturing Process: The process of making carbon fiber composite cylinders is more complex than manufacturing steel or aluminum cylinders. This complexity can contribute to the higher cost and may also require more specialized maintenance and testing protocols to ensure safety and performance over time.
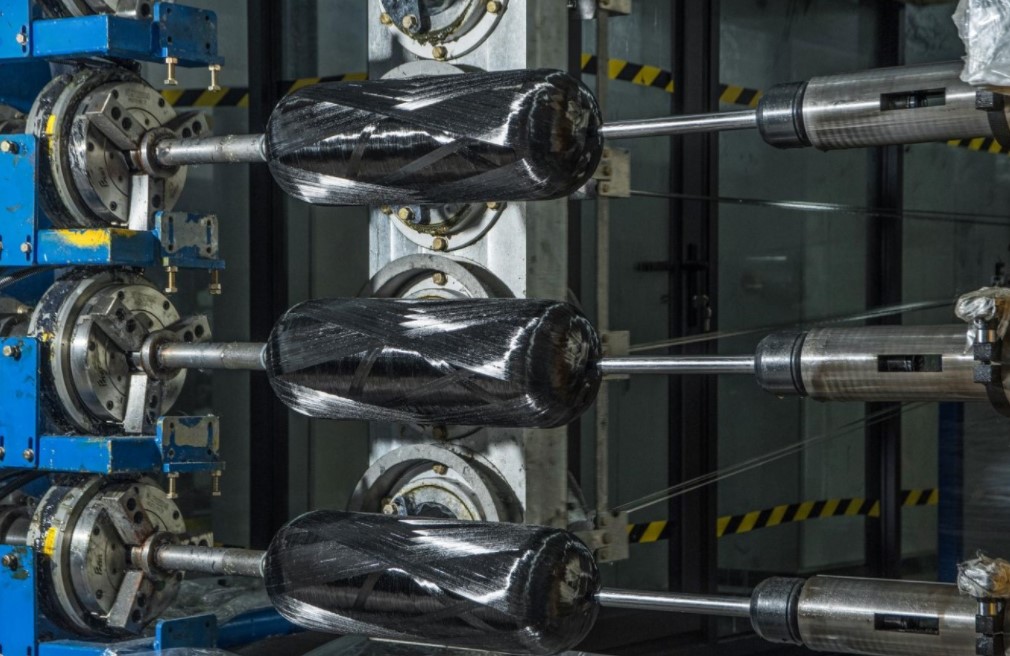
How Carbon Fiber Composite Cylinders Are Made
The manufacturing of carbon fiber composite cylinders involves several stages, each of which is crucial for ensuring that the final product is both lightweight and strong enough to handle the pressures it will face in real-world use.
- Liner Production: The process begins with the production of the inner liner, which can be made from aluminum or plastic. This liner serves as the airtight container that holds the compressed air.
- Fiber Winding: The next step is to wrap the liner with layers of carbon fiber. The carbon fibers are soaked in resin and then wound around the liner using precision machinery. This step ensures that the fibers are evenly distributed, which is essential for the strength of the cylinder.
- Curing: Once the fibers are in place, the cylinder is cured in an oven, where the resin hardens and bonds the fibers together. This process gives the cylinder its final strength and rigidity.
- Testing: After curing, the cylinder undergoes rigorous testing to ensure that it meets safety and performance standards. This typically includes hydrostatic testing, where the cylinder is pressurized with water to a level higher than its normal operating pressure to check for leaks or weaknesses.
Applications and Use Cases
Carbon fiber composite cylinders are used in a variety of applications, including:
- SCBA Systems: Firefighters and rescue workers rely on SCBA systems with carbon fiber composite cylinders because of their lightweight and high-pressure capabilities, allowing them to carry more air while remaining mobile.
- Diving: Scuba divers also benefit from carbon fiber cylinders, which allow them to carry enough compressed air for longer dives without being weighed down by heavier materials.
- Medical Oxygen Cylinders: In medical settings, lightweight composite cylinders are often used for portable oxygen supplies, as they are easier to transport than traditional steel or aluminum cylinders.
Conclusion
Breathing apparatus cylinders are made from a variety of materials, each with its advantages and drawbacks. Steel and aluminum are traditional materials that offer durability and affordability, but carbon fiber composite cylinders have become increasingly popular due to their lightweight and high strength. These cylinders provide an optimal balance of performance and mobility, making them ideal for demanding applications like firefighting, rescue operations, and diving. While carbon fiber composite cylinders may come with a higher price tag, their benefits in terms of weight reduction and long-term durability often make them the preferred choice for professionals who depend on their equipment in life-or-death situations.
Post time: Aug-21-2024