Introduction
In recreational and professional sea diving, the air tank is one of the most essential pieces of safety equipment. Traditionally, scuba tanks have been made from steel or aluminum due to their strength and availability. However, the emergence of carbon fiber composite tanks offers a new option that brings several advantages in terms of weight, durability, and efficiency. This article explains why carbon fiber air tanks are becoming more relevant for divers, highlights their benefits, and outlines key points to consider for their use and maintenance.
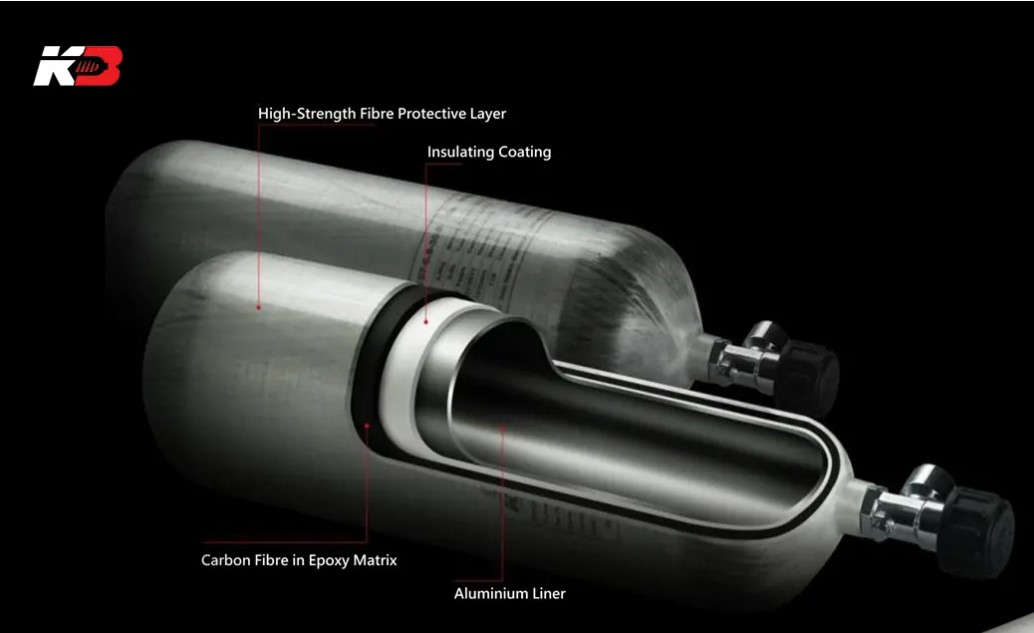
What Is a Carbon Fiber Air Tank?
Carbon fiber air tanks are high-pressure gas storage vessels made by wrapping layers of carbon fiber composite around a liner, which is typically aluminum or plastic. These tanks are often coated with resin for added durability and are designed to hold compressed air at pressures commonly around 3000 to 4500 psi. The carbon fiber wrapping provides strength while keeping the tank lightweight.
Why Use Carbon Fiber Tanks for Sea Diving?
Carbon fiber tanks are being increasingly considered for scuba diving due to several practical advantages:
1. Lighter Weight Means Easier Handling
Compared to steel tanks, carbon fiber tanks can weigh up to 50% less. This makes them easier to carry, wear, and maneuver both above and under water. Lighter gear is especially beneficial for shore divers, dive instructors, or divers with smaller body frames, reducing physical strain and fatigue.
2. Higher Air Capacity at Similar or Lower Weight
Because carbon fiber tanks can handle higher pressures, they can store more air without significantly increasing in size or weight. This means longer dive times or more efficient air reserves, which is especially useful during deep or technical dives.
3. Corrosion Resistance
One of the limitations of steel tanks is their vulnerability to rust, especially in salty marine environments. Carbon fiber tanks, particularly those with a non-metallic liner, are much more resistant to corrosion. This can extend the lifespan of the tank with proper care.
4. More Comfortable Diving Experience
Because of their lighter weight, carbon fiber tanks help divers maintain better buoyancy control. This can contribute to more stable, comfortable, and energy-efficient dives.
Key Considerations for Divers
Despite the advantages, carbon fiber tanks also require specific attention in use and maintenance. Here are some important things to keep in mind:
1. Cost vs. Benefit
Carbon fiber tanks are more expensive than aluminum or steel tanks, both in terms of initial purchase and sometimes in servicing. Divers need to consider whether the weight savings and performance justify the higher cost based on their frequency and type of diving.
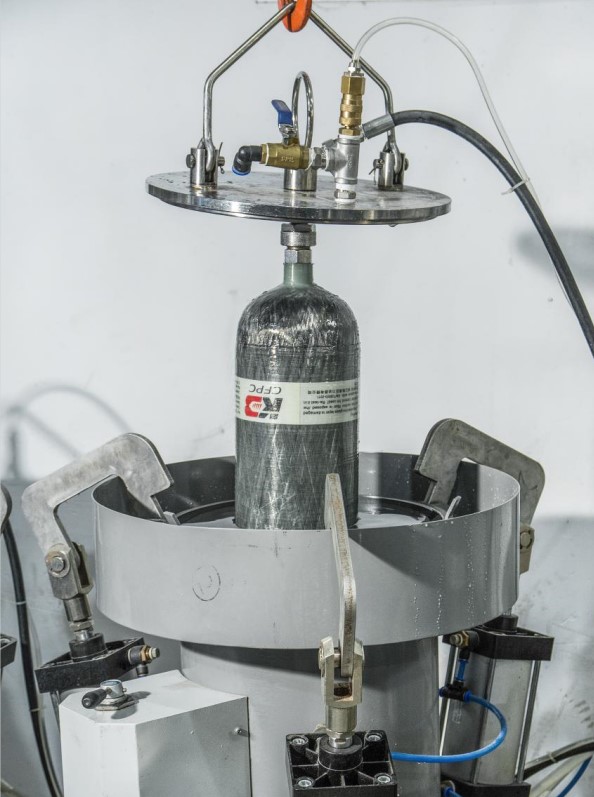
2. Inspection and Certification
Due to their construction, carbon fiber tanks have specific inspection and testing requirements. Many countries require hydrostatic testing every 3 to 5 years and regular visual inspections. Not all dive shops may have the equipment or certification to inspect carbon fiber tanks.
3. UV and Impact Sensitivity
The outer composite shell can degrade under direct sunlight (UV) or from physical damage. Most carbon fiber tanks have a protective resin or fiberglass wrap, but users should avoid dropping the tanks or leaving them exposed to sunlight for extended periods.
4. Limited Service Life
Unlike steel tanks, which can last for decades with good maintenance, carbon fiber tanks typically have a service life of 15 to 20 years. Some models may have a manufacturer-mandated retirement age regardless of condition.
5. Buoyancy Characteristics
Carbon fiber tanks tend to be more positively buoyant than steel tanks, especially as they empty. Divers may need to adjust their weight systems to account for this change in buoyancy.
Best Practices for Use and Maintenance
To get the most out of carbon fiber diving tanks, divers should follow these guidelines:
- Storage: Keep tanks in a cool, dry, and shaded place. Avoid direct exposure to the sun or high heat.
- Handling: Use protective boots or covers to avoid scratching or damaging the composite surface.
- Transportation: Secure the tank properly in vehicles or boats to prevent impact.
- Refilling: Always refill tanks at certified dive shops that understand the pressure ratings and care needed for composite materials.
- Regular Checks: Perform visual inspections regularly, checking for dents, cracks, delamination, or any changes in color or surface.
Other Considerations
- Compatibility: Ensure your dive gear is compatible with high-pressure tanks, particularly regulators and gauges.
- Training: New users may benefit from understanding the handling differences between composite and traditional tanks, especially for buoyancy and weight adjustment.
- Environmental Conditions: In extremely cold water, verify that the composite tank performs reliably, as some materials can behave differently in low temperatures.
Conclusion
Carbon fiber air tanks offer a smart alternative to traditional scuba tanks for those looking to reduce weight, improve comfort, and avoid corrosion. While they come with higher upfront costs and some specific maintenance needs, their benefits are clear, especially for active and experienced divers. With proper handling and care, carbon fiber tanks can enhance safety, performance, and enjoyment during sea diving adventures.
As diving equipment evolves, the use of carbon fiber tanks is likely to become more common, particularly for those who prioritize portability and advanced performance underwater.
Post time: Apr-14-2025